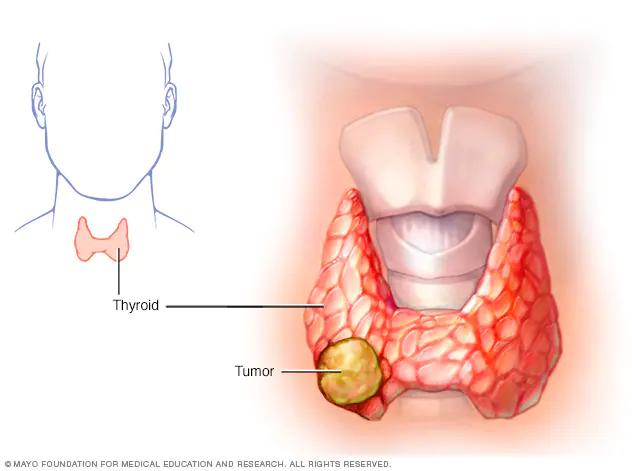
Thyroid Cancer
Made By Dawson J.
Thyroid Cancer Statistics (2024)
New Cases: Approximately 44,020 (12,500 in men and 31,520 in women)
Deaths: Approximately 2,170 (990 in men and 1,180 in women)
Average Diagnosis Age: 51 years
Gender Disparity: Nearly 3 times more common in women
Racial Disparity: 40% to 50% less common in Black people than in other racial or ethnic groups
Male vs Female Cancer Cases (2024)
Thyroid cancer occurs significantly more in women than in men.The exact reasons for this gender gap remain under study, but it is currently belived that hormonal differences may play a role.
Who Does This Cancer Affect?
Thyroid cancer can affect people of all ages but is most often diagnosed between ages 30 and 60. Women are about three times more likely to develop the disease than men. It is also less common in Black people, with rates about 40% to 50% lower than in other racial groups. These disparities may be due to a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Risk Factors and Causes
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing thyroid cancer. Women are at higher risk, especially during middle age, and those with a family history of thyroid cancer are more vulnerable. Other risk factors include exposure to radiation, obesity, and hereditary conditions like MEN2 and FAP. Both low and high iodine levels in the diet can also influence risk. Many cases are linked to genetic mutations acquired during a person’s life.
Symptoms
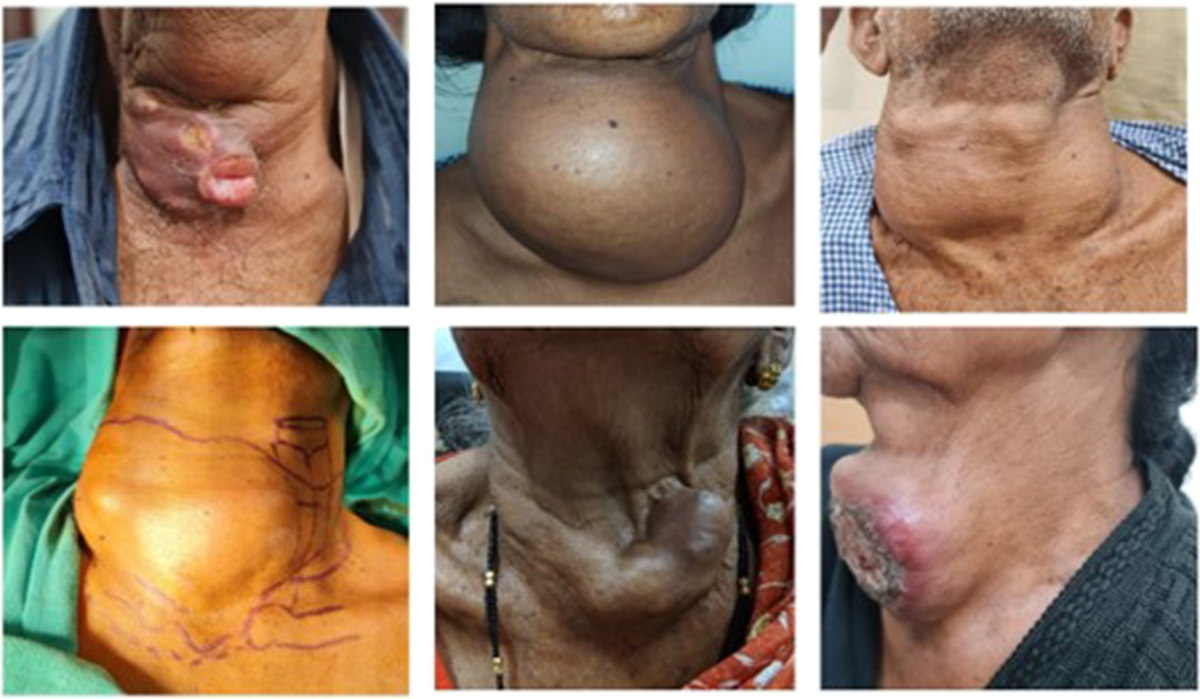
Thyroid cancer symptoms are often mild or absent in early stages. Common signs include a lump in the neck, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing. Swelling in the neck and persistent throat pain can also occur. These symptoms can be caused by other conditions, so medical evaluation is needed for proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several methods to diagnose thyroid cancer. These include physical exams to check for lumps, blood tests to measure thyroid function, and imaging techniques like ultrasounds. A biopsy, where a sample of thyroid tissue is examined, is often used to confirm the diagnosis.
Survival and Treatments
Thyroid cancer generally has a high survival rate, with most cases being treatable. Treatment options include surgery to remove the thyroid gland, radioactive iodine therapy, and hormone therapy. In advanced cases, chemotherapy or targeted therapies may be used.
Current Research
Current research focuses on understanding genetic mutations linked to thyroid cancer. Scientists are developing targeted therapies that minimize side effects while effectively treating the disease. Efforts are also underway to improve early detection methods, such as advanced imaging techniques. These advancements aim to improve survival rates and reduce the burden of treatment.
Interesting Facts
Thyroid cancer is one of the fastest-growing cancers in terms of diagnosis rates. Despite this, it has one of the lowest mortality rates among all cancers. Women are significantly more affected, but men tend to have worse outcomes. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in metabolism, which makes early treatment important for overall health.
Prevention
While not all thyroid cancer cases can be prevented, there are steps to reduce risk. Maintaining a healthy diet with balanced iodine levels is important. Avoiding unnecessary exposure to radiation, such as repeated medical imaging, can also help. Keeping a healthy weight and regular check-ups may lower the likelihood of developing thyroid cancer.
The Future
The future of thyroid cancer treatment looks promising with advances in medicine. Genetic testing is expected to play a larger role in both prevention and treatment. Research is focused on creating therapies tailored to individual patients, reducing the need for invasive procedures.
Pictures
Sources
American Cancer Society Statistics